-
English
-
French
-
Korean
-
Portuguese
-
Russian
-
Spanish

English

French

Korean

Portuguese

Russian

Spanish
Grid outages are becoming more frequent across the world. From Africa's load-shedding to Europe's winter grid stress and Asia's extreme-weather events, resilience is no longer optional—it is the core reason many factories, logistics parks, and commercial buildings invest in energy storage systems (ESS).
But what actually happens inside a modern ESS the moment the grid goes down? What does the PCS “see”? How fast does the STS respond? How do PV, diesel generators, and battery modules work together during those critical seconds?
Let's walk through the behind-the-scenes process—step by step—based on modern microgrid architecture in 2025.
Every ESS constantly monitors grid voltage, frequency, phase angle, and waveform distortion. A typical threshold for “grid abnormality” is:
The moment any of these exceed limits, the PCS flags a disturbance.
Detection time: ⏱ < 2 ms (typical for modern DSP-based control boards)
This early warning is crucial—milliseconds matter.

A modern microgrid uses an STS (Static Transfer Switch) to disconnect the load from the failing grid.
Why STS? Because mechanical switches are too slow.
In practice, high-performance STS in C&I microgrids can achieve:
➡️ 4–8 ms real switching time
For the factory, the lights don't flicker. For servers, PLCs, EV chargers, and industrial equipment, it feels like nothing happened.
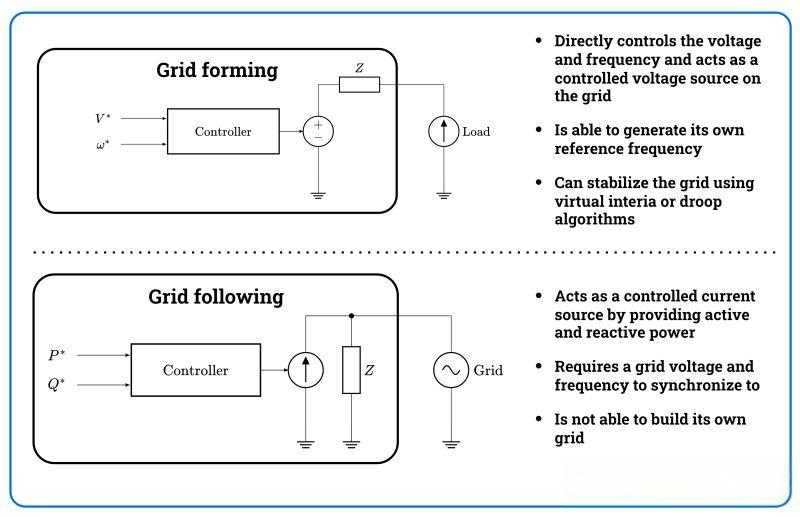
Once isolated, the ESS must form a new microgrid instantly.
The PCS switches from:
⚡ Grid-following mode → Grid-forming mode
In grid-forming mode, it must provide:
Essentially, the PCS becomes a virtual power plant inside the building.
This transition typically completes within 10–20 ms, thanks to modern fast-response vector-control algorithms.
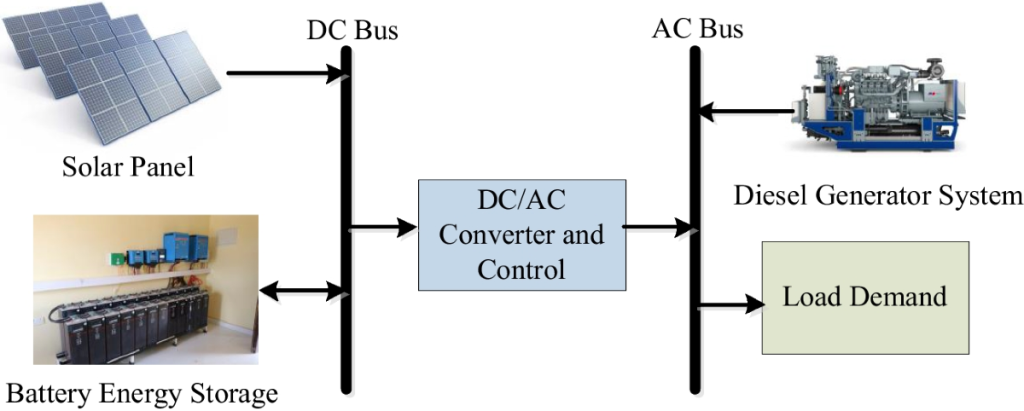
Once the microgrid stabilizes, the EMS activates its off-grid optimization logic:
The EMS maximizes solar output to support loads:
MPPT modules continue working normally in the microgrid.
Battery output is adjusted every 100–200 ms via droop curves.
High-C-rate LFP cells (like today's 280–314 Ah ESS cells) provide very stable off-grid performance and low-voltage sag.
EMS starts the genset only if:
This hybrid logic ensures both cost efficiency and longevity.
During outages, the EMS may automatically cut noncritical loads based on preset priority levels.
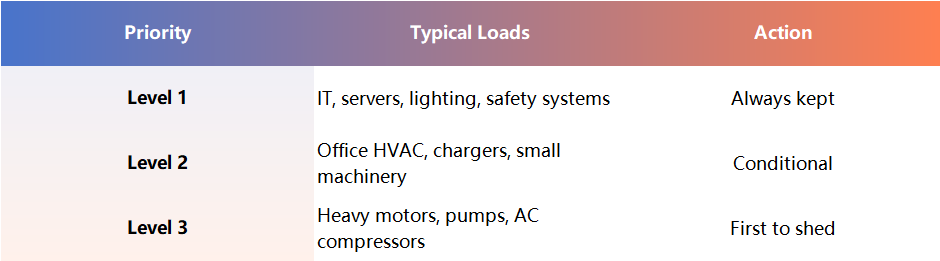
This prevents system overload and keeps the microgrid stable.
Once the grid recovers, reconnection is not immediate.
IEEE 1547 and many national grid codes require:
The PCS then synchronizes:
After synchronization, the STS closes the loop and loads transfer back to the grid.
Total reconnection time is typically 5–10 minutes.
The entire process—from outage detection to forming a stable microgrid—happens in under 20 milliseconds. This level of resilience used to require diesel microgrids or UPS systems. Now, ESS replaces both.
For countries with unstable grids—South Africa, Kenya, Pakistan, Iraq, the Philippines—this capability is not a luxury. It is the core value of C&I energy storage deployment.
And as more factories combine:
…the future of energy resilience lies in next-generation hybrid microgrids, not just batteries.
Explore the latest news and technology trends in the energy storage industry.

